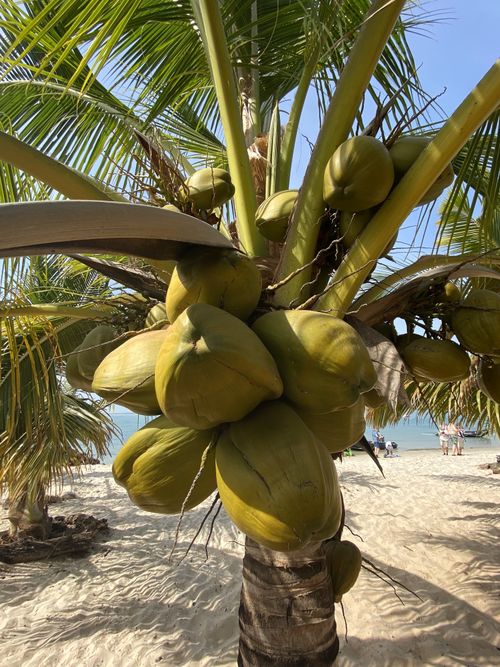
Coconut meat, also known as coconut flesh, begins its journey as a liquid called endosperm. This liquid fills the coconut during its early stages of growth and gradually solidifies into the white, edible flesh we know. The transformation of coconut water into coconut meat is a fascinating process. As coconuts mature, the liquid endosperm changes into a nutrient-dense food with many applications across the globe.
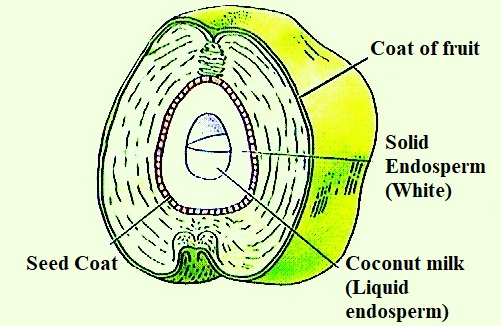
What is Liquid Endosperm?
The formation of coconut meat begins with the absorption of liquid endosperm, a nutrient-rich fluid that enters the coconut tree through its roots. As a coconut develops, the liquid endosperm fills the cavity inside the coconut, surrounding the seed.
This liquid, which is commonly referred to as coconut water, is high in nutrients and plays a crucial role in the development of the coconut seed. Over time, this liquid starts to undergo a significant transformation, leading to the creation of the solid, white flesh known as coconut meat.
The Role of Liquid Endosperm in Coconut Growth
Coconut water, or liquid endosperm, is rich in cytokinins, proteins, sugars, vitamins, and minerals. These components are vital to the growth and maturation of the coconut. The endosperm acts as a food reservoir for the developing embryo within the coconut, ensuring it receives the nutrients it needs to grow and mature into a full-grown seed.
In the early stages of the coconut’s life cycle, the entire cavity is filled with liquid endosperm, providing essential sustenance for the plant. As the coconut matures, however, the liquid endosperm begins to undergo a biochemical transformation.
How Liquid Becomes Solid Coconut Meat
As the coconut matures, the once-liquid endosperm starts to deposit on the inner walls of the coconut shell. This deposition forms a thin, white layer, which gradually thickens over time. The transformation is driven by a combination of factors, including age of the coconut, temperature, and enzymatic activity within the fruit.
The endosperm solidifies due to the accumulation of cellulose fibers, lipids, and other organic compounds that crystallize as the coconut ages. This process can take several months, during which the coconut meat thickens and becomes denser, eventually forming the solid, edible flesh that we harvest from mature coconuts.
From Liquid to Solid: The Maturity Stages
Young Coconut (Green Stage): At this point, the coconut contains mostly liquid with very little solid meat. The small amount of meat is soft and jelly-like, often referred to as young coconut meat.
Semi-Mature Stage: As the coconut continues to grow, the meat becomes firmer and the water content reduces. The coconut can now provide both water and solid flesh. The meat starts to gain more flavor and density.
Fully Mature Stage: In the final stage, the coconut has a thick layer of solid meat with only a small amount of water remaining. This is the stage when coconuts are harvested for products like coconut oil, desiccated coconut, and other food items.

Nutritional Benefits of Coconut Meat
As the coconut meat forms, it also gains significant nutritional value. Mature coconut meat is packed with healthy fats, especially medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs). These fats are easily digestible and provide a quick source of energy. Furthermore, coconut meat is rich in fiber, which supports digestion. It also contains important vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, potassium, and magnesium.
Coconut Meat vs. Coconut Water
While coconut water is known for its hydration and electrolyte balance, coconut meat is a more energy-rich food. The meat contains more calories due to its fat content, making it a great source of long-lasting energy. In addition, the meat provides more fiber than the water, which aids in digestion and supports overall gut health.
Uses of Coconut Meat
The journey of coconut meat, from the solidification of liquid endosperm to its mature form, opens the door to a wide array of culinary, cosmetic, and industrial uses. Mature coconut meat is harvested for various purposes, making it one of the most versatile natural products.
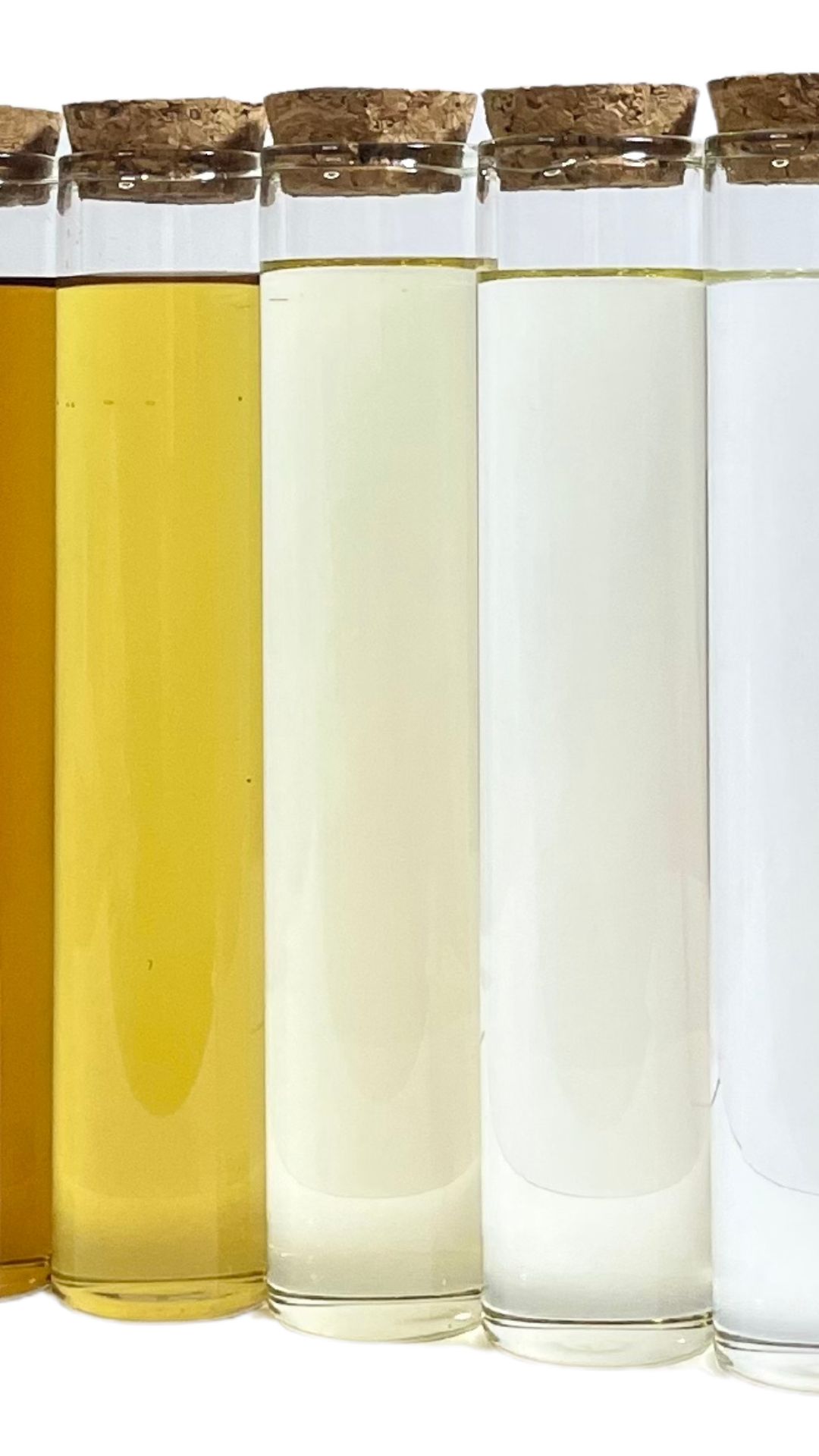

Culinary Uses
Coconut meat is a staple ingredient in many tropical and Asian cuisines. Some common culinary uses include:
Coconut Milk and Cream: Grated coconut meat is pressed to extract coconut milk, which is used in a variety of dishes such as curries, soups, and desserts. Coconut cream, a thicker version, is prized for its rich texture and is often used in creamy sauces and desserts.
Desiccated Coconut: This is a dried and grated form of coconut meat used in baking and as a topping for desserts and savory dishes. Desiccated coconut can be fine, medium, or coarse, depending on the intended use.
Coconut Oil: Extracted from the mature coconut meat, coconut oil is a popular cooking oil known for its high smoke point and health benefits. It is also a key ingredient in various beauty products due to its moisturizing properties.
Coconut Flour: The dried pulp left over from extracting coconut milk can be ground into a fine flour, which is often used as a gluten-free alternative in baking.
Cosmetic and Industrial Uses
Coconut meat is also used to produce virgin coconut oil, which has numerous applications in the cosmetic industry. It is known for its antimicrobial and moisturizing properties, making it a popular ingredient in skin creams, lotions, and hair treatments.
In addition to beauty products, coconut oil derived from the meat is used in soap-making and in producing eco-friendly cleaning products.
Sustainability and Coconut Meat
The entire coconut tree, including its fruit, is highly sustainable. The journey of coconut meat, from liquid endosperm to its solid form, not only yields an abundance of products but also ensures that nothing goes to waste. Coconut shells can be used as natural bowls or processed into activated carbon, while the husks can be converted into coir, a natural fiber used in mats, ropes, and brushes.
Coconuts grow abundantly in tropical regions, and many of the world’s largest coconut-producing countries, including the Philippines, Indonesia, and India, have invested in sustainable farming practices to meet global demand while protecting their natural resources.
Conclusion

The journey of coconut meat from liquid endosperm to solid, edible flesh highlights the coconut’s adaptability and versatility. Starting as a refreshing drink, it eventually transforms into a nutritious food used in diets worldwide. Whether for culinary or cosmetic purposes, coconut meat has a significant role in various industries. As demand for coconut-based products grows, understanding this natural process enhances our appreciation for the value it brings to everyday life.
Luxenature Indonesia, a leading exporter and supplier of coconut products, provides all variants of coconut meat, from semi-husked coconut to edible copra, coconut oil, desiccated coconut, nata de coco, coconut cream, and coconut milk. With a strong commitment to quality and sustainability, Luxenature Indonesia caters to diverse global demands. We are your reliable partner for sourcing premium coconut products, ensuring quality and sustainability in every product we offer.
For inquiries and more information, contact us at Luxenature and let’s grow your business with our premium coconut products.

